Treatment of tendonitis in the shoulder




Definition of treatment for tendinitis in the shoulder
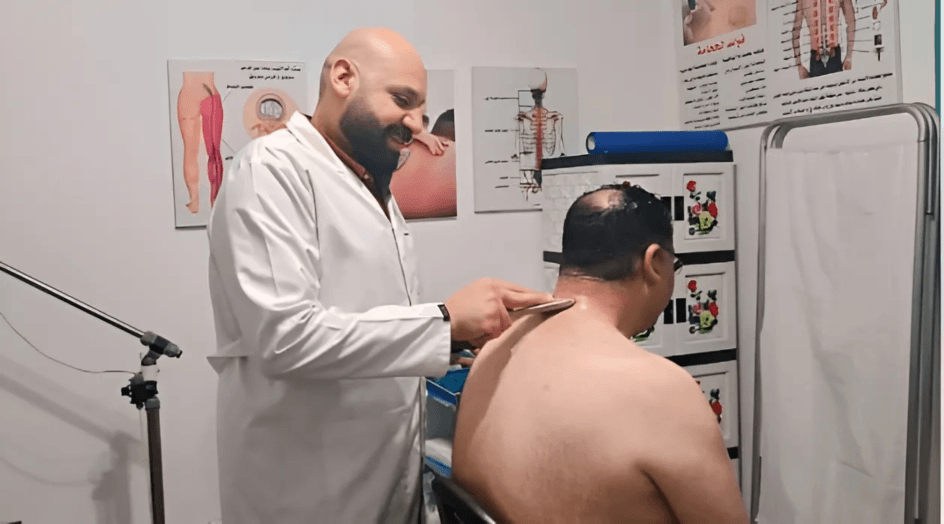
Shoulder tendinitis is a common problem that causes pain and difficulty moving the shoulder joint. Although this inflammation can resolve on its own over time, persistent pain may require effective treatment to restore full comfort and movement. At our center, we offer a comprehensive range of physical therapy solutions to relieve tendinitis and rehabilitate the shoulder using the latest advanced medical techniques and equipment.
For reservations and communication
Causes of tendonitis in the shoulder
Repetitive stress: Performing repetitive movements using the shoulder, such as lifting weights or sports activities that require repetitive movement.
Aging: The tendon becomes less flexible as you age, making it more susceptible to injury.
Direct injuries: Exposure to a direct injury to the shoulder, such as a fall or a strong impact.
Poor posture: Poor posture while sitting or working for long periods of time can put stress on the tendons.
Symptoms of tendonitis in the shoulder
- Shoulder pain that increases with joint movement, especially when raising the arm.
- Swelling of the shoulder with redness in some cases.
- Difficulty moving the shoulder, and feeling sharp pain when trying to make certain movements.
- Muscle weakness, which makes daily activities difficult.
- Pain when sleeping on the affected shoulder, which affects the quality of sleep.
Treatment of tendonitis in the shoulder
- Painkillers: Use painkillers such as Paracetamol, Naproxen, or Ibuprofen to relieve pain and swelling.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy sessions include stretching and strengthening exercises for the shoulder muscles to restore normal movement and relieve pain. Advanced techniques such as ultrasound and laser therapy are also used.
- Cortisone injections: These injections are used to reduce inflammation and pain, especially in severe cases that have not responded to other treatments. Such as Methylprednisolone and Betamethasone.
- Additional tips to reduce inflammation: Rest and avoid strenuous activities, with the use of cold compresses to reduce pain.
Ensure correct body positions and avoid repetitive movements that strain the shoulder.
Do daily stretching exercises for the shoulders and arms, and it is preferable to consult a physical therapist to obtain appropriate exercises.
For reservations and communication